nmap service detection - a packet level analysis
NMAP packet analysis
nmap is arguably the most used tool for network discovery and port scanning. Its the first tool used in recon. Although it is used mostly just for port scanning, there are a ton of things it can do. I am not gonna go through it here, but man nmap is a good place to start (there is always something new I learn whenever I open the man page). In this post, My main goal is to understand at the network level how nmap detects services and their versions.
Setup:
I have two kali VMs running, one to run some services and another to run nmap and scan and detect these services.
I’ll start with a simple default scan without any options. I’ll run a simple web server on a non standard port to see if nmap can detect the service without any scripts/ probes. Next, I explore what happens with -sV option and -sC option.
Default scan
Lets start off with the default scan without any scripts. I’ve started a python simplehttp server on port 81 on 10.0.2.12. python3 -m http.server 81. nmap is running on 10.0.2.15
nmap 10.0.2.12 -p 81
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2020-05-28 06:51 EDT
Nmap scan report for 10.0.2.12
Host is up (0.00061s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE
81/tcp open hosts2-ns
MAC Address: 08:00:27:B9:34:ED (Oracle VirtualBox virtual NIC)
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.31 seconds
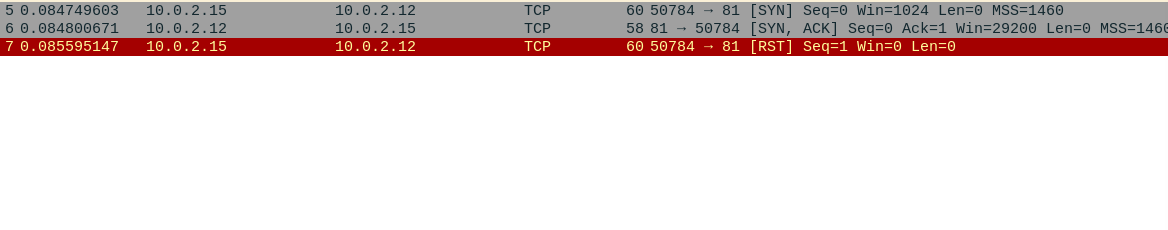
nmap just sends a SYN packet and if it receives a SYN ACK back, it confirms the port is open. TCP connection is not established here as nmap already got what it needed and it sends a RST packet to end the conversation. It looks up the service associated with that port in /usr/share/nmap/nmap-services and reports it. In this case, its hosts2-ns
SYN scan is the default port scanning option with nmap. There are other options available
Service/ version detection using -sV
-sV option is used to detect the service running on the port and its version. Useful links here and here
I’ve started python http server like earlier but this time on port 999.
nmap -sV 10.0.2.12 -p 999
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2020-05-28 07:16 EDT
Nmap scan report for 10.0.2.12
Host is up (0.0010s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
999/tcp open http SimpleHTTPServer 0.6 (Python 3.7.3)
MAC Address: 08:00:27:B9:34:ED (Oracle VirtualBox virtual NIC)
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 11.83 seconds
At this point, we know how nmap checks if port is open. Here port 999 is open. Lets understand what nmap does next to find information about the service.
After nmap detects the port to be open, it establishes a TCP connection and waits for a few seconds to check if the service replies back with a welcome banner (some services do this). nmap matches this with signatures in /usr/share/nmap/nmap-service-probes to determine service. This file has tons of signatures matching replies from various services. Not all services give these welcome banners.
We can see this happen with ssh.
I’ve started ssh on a non standard port 960 (default port is 22, it can be changed in /etc/ssh/sshd_config). Lets examine the packets.
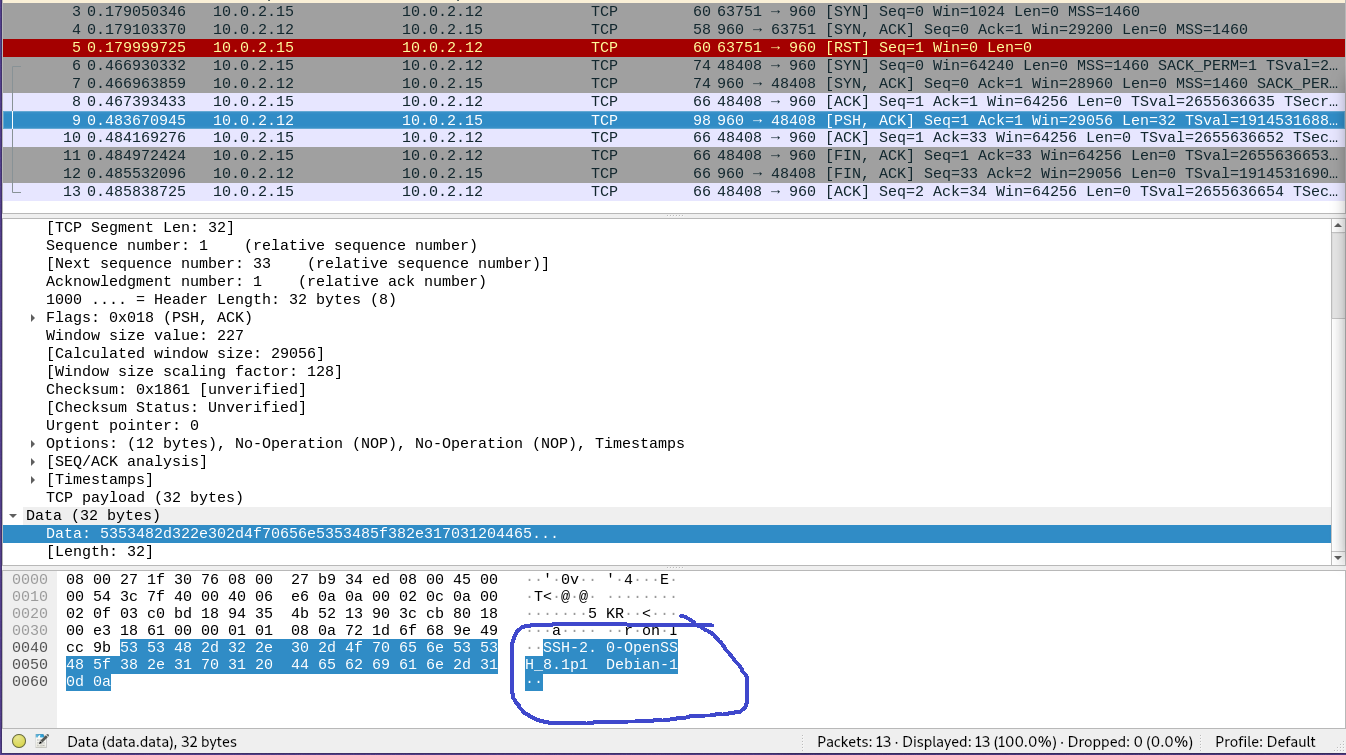
We can see on 9th packet, host (10.0.2.12) sends SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_8.1p1 Debian-1 without any request from nmap (10.0.2.15).
nmap gets all the needed information (service and version) from this packet, so it doesn’t send any probes after this, so it closes this connection. The initial port scan is done in the first three packets (3, 4, 5)
But not all services send such banners. In case of http, nmap waits for about 6 seconds to get any banner and then sends some random data and tries to match the response.
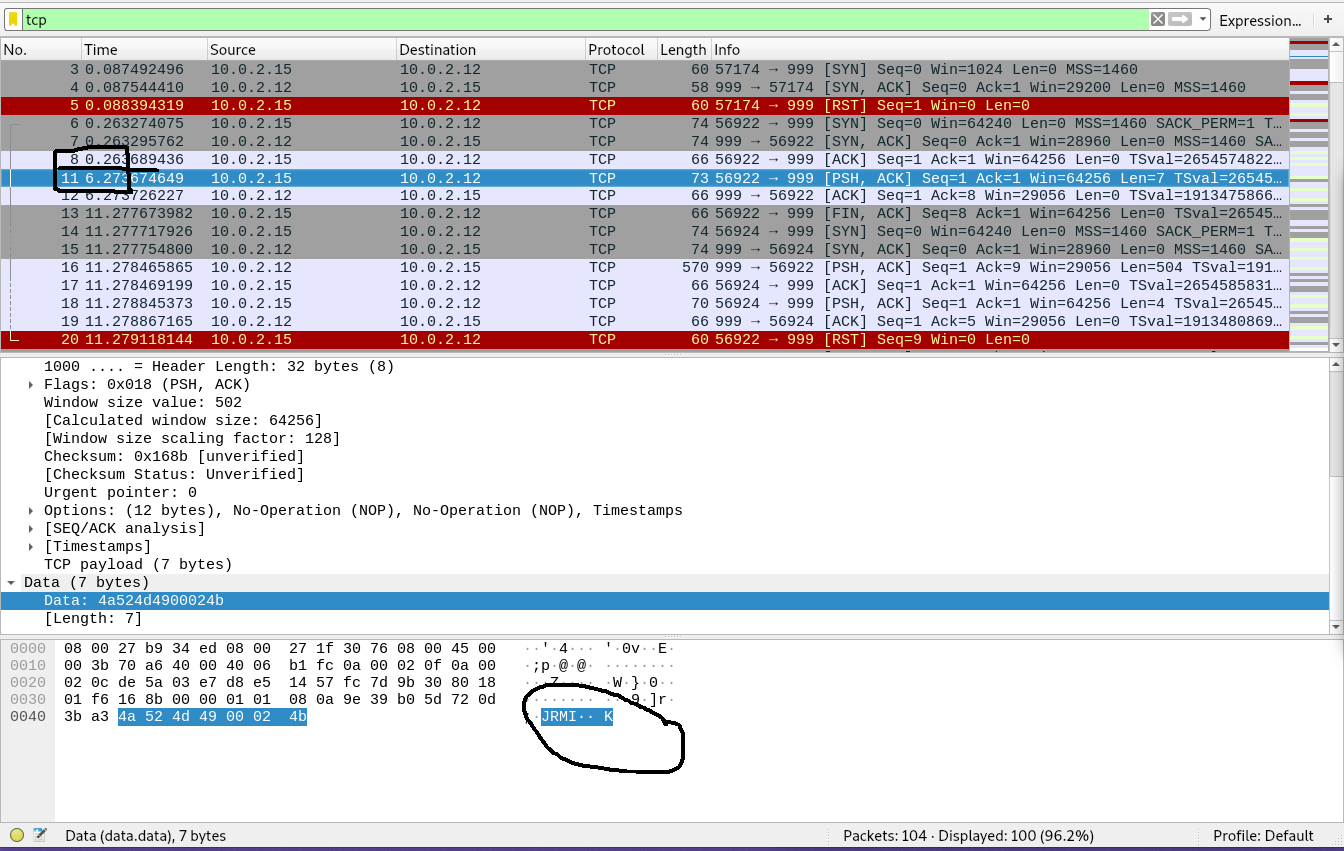
We can see that after initial connection, it sends random bytes (JRMI..K) in packet 11 And host replies to this with a http 400 error in packet 16. We can see the whole conversation with follow -> TCP stream (or “tcp.stream eq 1” filter)
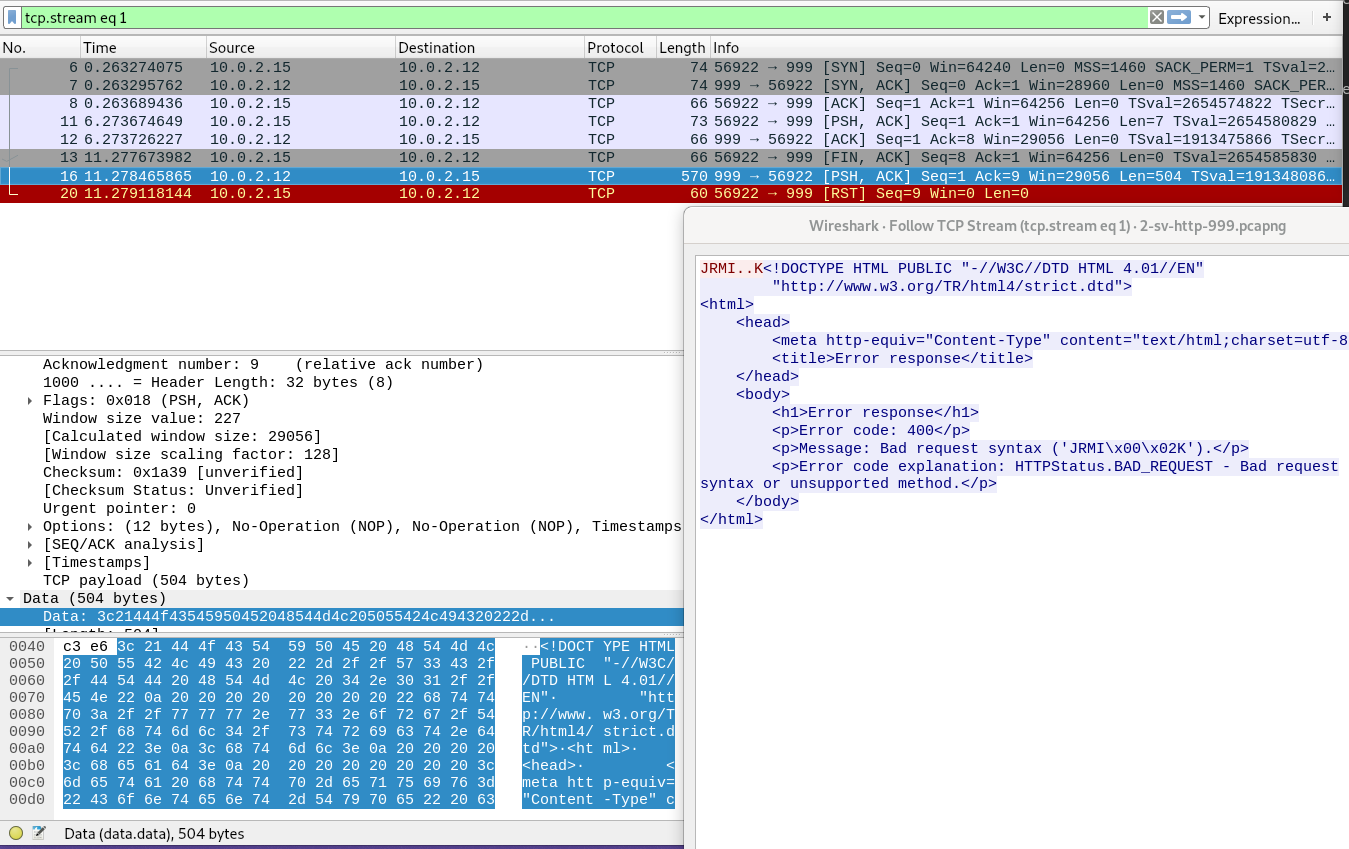
Now nmap knows http is running on this port. So next, it sends a bunch of http requests. http version can be extracted from the headers of the responses. These requests are sent by the .nse scripts (/usr/share/nmap/scripts) run by nmap. Debug flags can be added to get information about which scripts are running nmap -sV -d --version-trace 10.0.2.12 -p 999. Following output shows just the scripts part of whole debug log
NSE: Starting vmware-version M:55f671ba3738 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting http-trane-info M:55f671b86ef8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting hnap-info M:55f671b85ed8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting https-redirect M:55f671b87f18 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: [vmware-version M:55f671ba3738 10.0.2.12:999] Couldn't download file: /sdk
NSE: Finished vmware-version M:55f671ba3738 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Finished https-redirect M:55f671b87f18 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: [http-trane-info M:55f671b86ef8 10.0.2.12:999] Final http cache size (469 bytes) of max size of 1000000
NSE: [http-trane-info M:55f671b86ef8 10.0.2.12:999] HTTP: Host returns proper 404 result.
NSE: [hnap-info M:55f671b85ed8 10.0.2.12:999] HTTP: Host returns proper 404 result.
NSE: [http-trane-info M:55f671b86ef8 10.0.2.12:999] Final http cache size (938 bytes) of max size of 1000000
NSE: Finished http-trane-info M:55f671b86ef8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: [hnap-info M:55f671b85ed8 10.0.2.12:999] Final http cache size (1407 bytes) of max size of 1000000
NSE: Finished hnap-info M:55f671b85ed8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting http-server-header M:55f671c0e5a8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Finished http-server-header M:55f671c0e5a8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
The requests from these probes can be seen in the http traffic as well
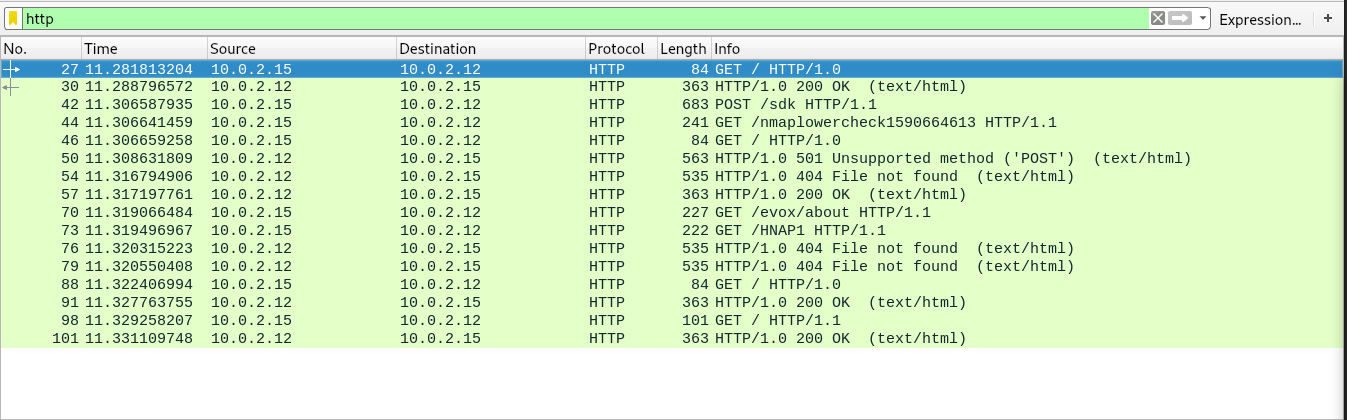
Default scripts using -sC
-sC option runs the default .nse scripts. Following is the part of debug log from the scan with debug flags for version tracing and script tracingnmap -sV -d --version-trace -sC --script-trace 10.0.2.12 -p 999
NSE: Starting address-info M:55ba29926dd8 against 10.0.2.12.
NSE: Finished address-info M:55ba29926dd8 against 10.0.2.12.
NSE: Starting hnap-info M:55ba29d042d8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting flume-master-info M:55ba28d7e638 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: [flume-master-info M:55ba28d7e638 10.0.2.12:999] HTTP GET 10.0.2.12:999/flumemaster.jsp
NSE: Starting http-generator M:55ba290cea08 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting hadoop-secondary-namenode-info M:55ba29fd5cb8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: [hadoop-secondary-namenode-info M:55ba29fd5cb8 10.0.2.12:999] HTTP GET 10.0.2.12:999/status.jsp
NSE: Starting http-svn-enum M:55ba29f559c8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting http-svn-info M:55ba28d9b998 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting http-cors M:55ba291345d8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting https-redirect M:55ba294fbd28 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting http-auth M:55ba29d05318 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting http-cookie-flags M:55ba291a97a8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: [http-cookie-flags M:55ba291a97a8 10.0.2.12:999] path script-arg is nil; checking / and anything from http-enum
NSE: [http-cookie-flags M:55ba291a97a8 10.0.2.12:999] start check of /
NSE: Starting hadoop-tasktracker-info M:55ba295e51b8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: [hadoop-tasktracker-info M:55ba295e51b8 10.0.2.12:999] HTTP GET 10.0.2.12:999/tasktracker.jsp
NSE: Starting http-webdav-scan M:55ba28c7bee8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting http-git M:55ba299bfdd8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting http-favicon M:55ba29135618 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting http-ntlm-info M:55ba2a2a87d8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting xmlrpc-methods M:55ba291e0dd8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting vmware-version M:55ba2a805408 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting hadoop-datanode-info M:55ba28b80988 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: [hadoop-datanode-info M:55ba28b80988 10.0.2.12:999] HTTP GET 10.0.2.12:999/browseDirectory.jsp
NSE: Starting http-title M:55ba294806b8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting http-ls M:55ba292a5248 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting http-robots.txt M:55ba29f54988 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting hbase-master-info M:55ba295e6208 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: [hbase-master-info M:55ba295e6208 10.0.2.12:999] HTTP GET 10.0.2.12:999/master.jsp
NSE: Starting hbase-region-info M:55ba29ec16c8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: [hbase-region-info M:55ba29ec16c8 10.0.2.12:999] HTTP GET 10.0.2.12:999/rs-status
NSE: Starting hadoop-jobtracker-info M:55ba28b819d8 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: [hadoop-jobtracker-info M:55ba28b819d8 10.0.2.12:999] HTTP GET 10.0.2.12:999/jobtracker.jsp
NSE: Starting hadoop-namenode-info M:55ba28b33158 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: [hadoop-namenode-info M:55ba28b33158 10.0.2.12:999] HTTP GET 10.0.2.12:999/dfshealth.jsp
NSE: Starting http-methods M:55ba292a6248 against 10.0.2.12:999.
NSE: Starting http-trane-info M:55ba28d9c438 against 10.0.2.12:999.
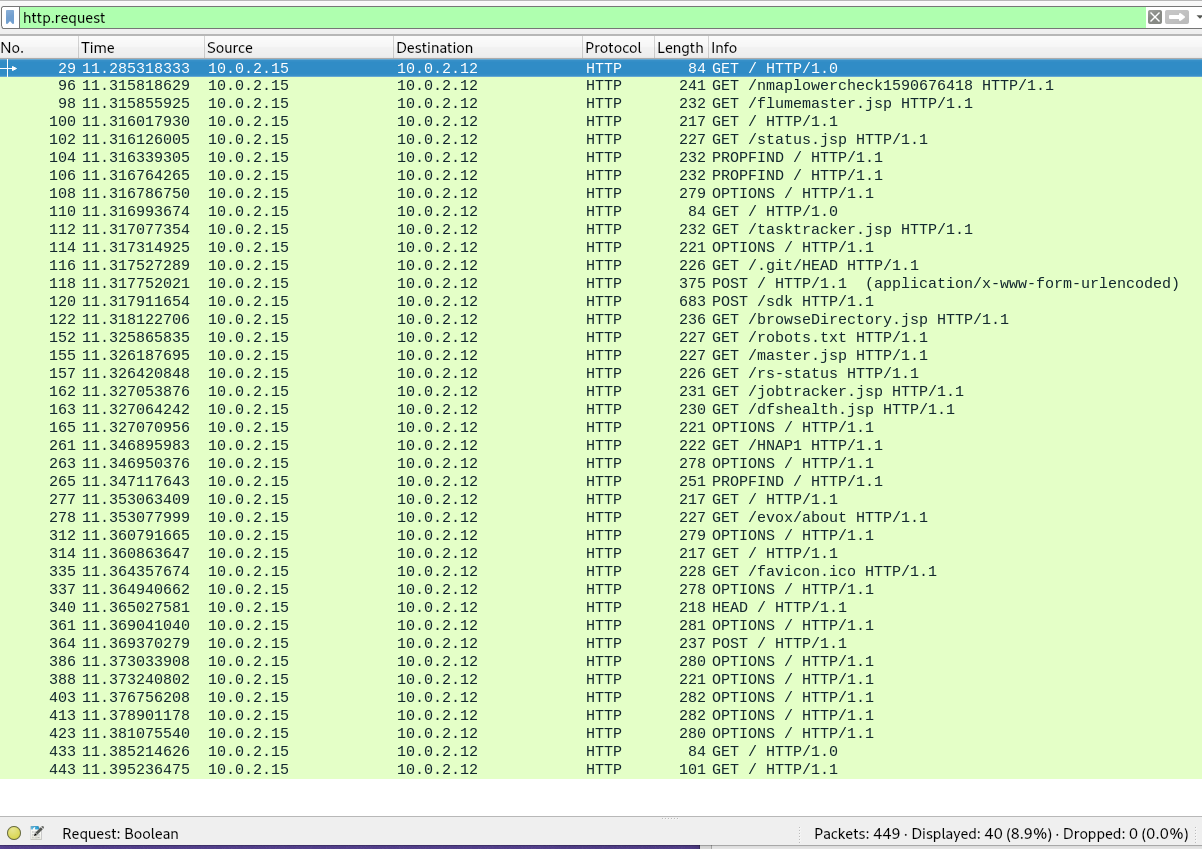
Lets examine some of the interesting requests from these logs belwo
Interesting Requests
PROPFIND / HTTP/1.1
This is http method for distributed authoring protocols like WebDAV, which allows clients to create, change and move documents on a server. Yes, it already looks shady - there are about 37 exploits on exploitdb already. According to the RFC, this http method is used to retrieve properties stored as XML from a web resource. Nmap uses this method in the request to detect webdav installations. Although webDAV is rarely used, its extension CalDAV is widely used to access a remote calendar (like google calendar)
This request is sent by “http-webdav-scan” script
GET /nmaplowercheck1590497863 HTTP/1.1
With this request, nmap checks if the server is returning a proper 404 error. The number after ‘nmaplowercheck’ is just the epoch time
GET /HNAP1 HTTP/1.1
HNAP protocol is used to remotely manage netowrk devices. The GET request to /HNAP1 is used to check if the protocol is being used on the host/router. The response for this request would be the basic device information and list of valid SOAP commands that can be sent to the device. This request is from the “hnap-info” script
- Preflight requests:
nmap sends a bunch of preflight requests, which use OPTIONS method to check if some methods are allowed in the requests before actually using the method.
OPTIONS / HTTP/1.1
Origin: example.com
Host: 10.0.2.12
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Nmap Scripting Engine; https://nmap.org/book/nse.html)
Access-Control-Request-Method: DELETE
Connection: close
This is one of such requests from nmap to check if DELETE method is allowed before using it.
POST / HTTP/1.1
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: 10.0.2.12
Content-Length: 88
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Nmap Scripting Engine; https://nmap.org/book/nse.html)
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Connection: close
<methodCall> <methodName>system.listMethods</methodName> <params></params> </methodCall>
system.listMethods is used to enumerate methods implemented by the XML-RPC server. It returns an arraay of strings, each of which is the name of a method implemented by the server. XML-RPC is a remote procedure call using xml encoding used by CMS frameworks like wordpress. It allows software running on different OS and different environments to make procedure calls over internet. XML-RPC for php comes with many vulnerabilities, which may prove very useful during recon.
POST /sdk HTTP/1.1
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<soap:Header>
<operationID>00000001-00000001</operationID>
</soap:Header>
<soap:Body>
<RetrieveServiceContent xmlns="urn:internalvim25">
<_this xsi:type="ManagedObjectReference" type="ServiceInstance">ServiceInstance</_this>
</RetrieveServiceContent>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
This is a SOAP request over http. This request with ‘/sdk’ uri is a query to get the basic information of VMware server running on the host. If vmware is running on server and, the response for this request would contain the vmware version information like server version, build, product line id. This is being requested by “vmware-version” script
-
GET /evox/about HTTP/1.1This request aims to get information from trane tracer SC devices, which are used to communicate with HVAC equipment controllers -
GETrequest to.git/HEADThis is done to check for a git repository in the website’s root directory. If it finds a HEAD file (which basically contains the git branch of the repo), it sends more such requests

Leave a comment